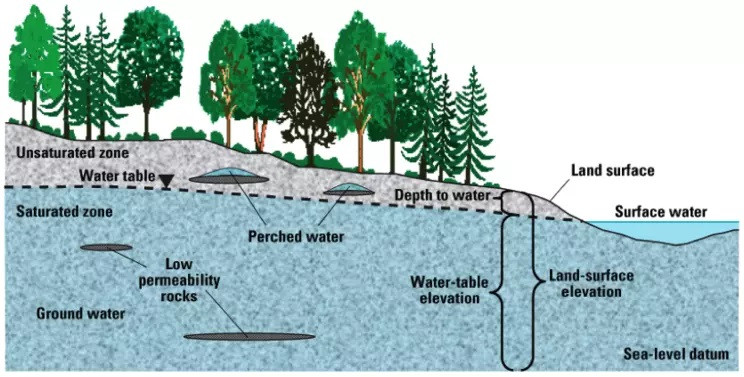
Chapter 2 focuses on aquifers and their main characteristics. It presents definitions of groundwater and aquifers, as well as the concepts of porosity and permeability, which are essential for understanding groundwater storage and flow in rocks. The chapter explains methods for measuring porosity, the role of grain-size distribution, and the classification of hydrogeological formations. It also describes the main types of aquifers: unconfined, confined, semi-confined (leaky), and perched aquifers.
- Teacher: Boualem BOUSELSAL
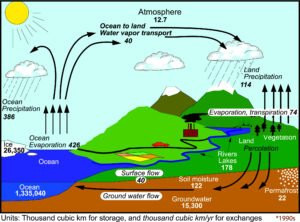
The hydrogeology course focuses on the study of water in the environment, particularly groundwater and its relationship with surface water. It covers the water cycle, global water reservoirs, watersheds and their hydrological behavior, as well as hydrological and hydrogeological balances. The course also examines aquifers, their functioning and management, and major water-related risks such as floods, with the aim of improving sustainable water resource management and environmental protection.
- Teacher: Boualem BOUSELSAL
