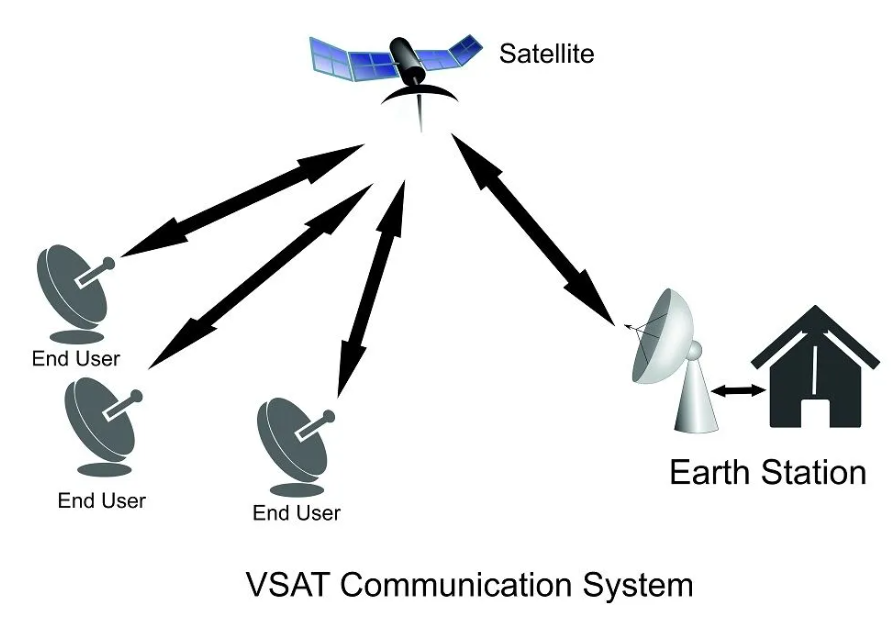
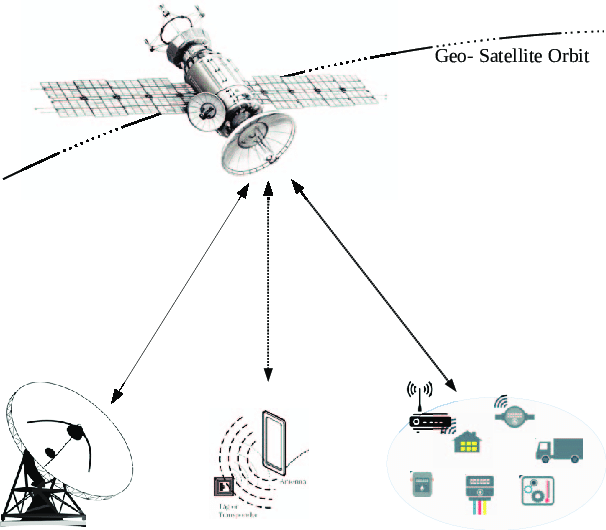
Very Small Aperture Terminal (VSAT) technology represents one of the most significant developments in modern satellite communications, particularly in regions lacking reliable terrestrial infrastructure. As the demand for fast, secure, and wide-coverage communication services increases, VSAT systems have emerged as an effective solution, offering users data, voice, and internet connectivity over vast geographical areas. Their relatively small antenna size, ease of installation, and reduced operational cost have made them highly suitable for commercial, governmental, and industrial applications.
Despite their compact design, VSAT stations operate within a larger satellite communication network and rely on a central ground station known as a Hub. The Hub manages network configuration, controls traffic, monitors terminal performance, and ensures service reliability. As a result, VSAT technology plays a crucial role in extending global communication capabilities, supporting remote communities, financial networks, research institutions, and many other critical services.